Marketing attribution has grown importance over the years, as many digital marketers and website owners are looking to stretch every dollar being spent and prioritize multi-channel marketing efforts across various digital marketing channels, i.e. eDMs, Organic Search, PPC, Social Media, Display Advertising.
What is marketing attribution?
It is a measurement-centric method of allocating the credit to marketing channels or touch points that leads to a desired action on your website – for example: making a purchase, sending an inquiry email, subscribing newsletters.
It is important for you to understand how each marketing attribution model works, before diving in to judge the performance of your marketing campaigns. By using the below scenario as an example, this will give you an insight on how each attribution model works, and allows you to make better marketing decisions.
Scenario Example
On Day #1: User wants to purchase a coffee table for his new house, and perform a keyword search on Google. He clicks on one of the organic listing on Google Search Engine Result Page (SERP) to land onto Overstock.com.
On Day # 2: He continues his search for his coffee table, and clicks on one of the PPC ads on Google SERP to land onto Overstock.com again. He subscribes to the email newsletter this time.
On Day #3: He receives an eDM from Overstock.com with a promotional offer of 30% discount sale, and clicks the “Buy Now” button from the eDM to enter the website. Unable to resist the discount offer, he decides to make a purchase of the furniture from the website.
1. First touch attribution
This attribution model focuses on the first marketing channel or touch point that brings the sales conversion. Therefore, the organic search channel gets the credit based on the above scenario example.
2. Last touch attribution
This works on the contrary to the first touch attribution, as the eDM campaign gets the credit for driving in the sales purchase. Google Analytics adopts the last touch attribution in measuring conversions based on marketing channels.
3. Multiple touch attribution
For this case, credit is given to multiple marketing channels or touch points that assisted and drove the sales conversion. Therefore, all the 3 touch points:, organic search, PPC ad campaign and eDM campaign gets one point each. An example of such attribution model is the Multi Channel Funnel (MCF) report in Google Analytics.
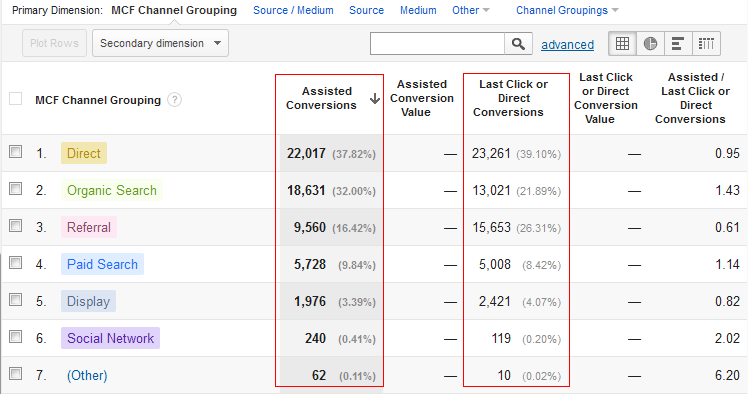
In the below screen capture of MCF report, the “Assisted Conversions” column contains the number of conversions for which this marketing channel or touch point contributed to the conversions, but doesn’t includes the final/last touch point credit count. The “Last Click or Direct Conversions ” column contains the number of conversions for which this channel was the final/last touch point that contributed to the conversion.